More Information Interface
What You See
The interface labeled "More Information" displays fields for "Configuration," "TCP Speed," and "Simulation Time." The "Configuration" field shows a string of alphanumeric characters, robot state codes ("S00110 T000010"), "TCP Speed" is set at "0 mm/s," indicating the current speed of the Tool Center Point, and "Simulation Time" is recorded as "0 s."
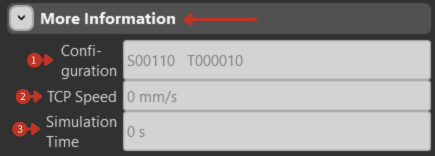
System status and configuration details for robot operation
What It Means
This part of the interface provides supplemental details related to the robot's operational status and simulation metrics, which are vital for diagnostics and process monitoring.
Configuration Field
"Configuration" Field: Likely represents specific configuration states or conditions of the robot, which could include axis positions, tool states, or program steps. This information is critical for understanding the robot's current setup and preparing for task execution or troubleshooting.
State Codes Breakdown:
-
S00110: Singularity configuration
- Each digit represents a joint state
- Used for path planning
- Important for avoiding singularities
-
T000010: Turn configuration
- Indicates joint turn counts
- Relevant for robots with infinite rotation
- Affects path calculation
TCP Speed Reading
"TCP Speed": Shows the current or last recorded speed of the robot's TCP.
- "0 mm/s" indicates stationary state
- Updates in real-time during movement
- Useful for monitoring actual vs. programmed speeds
- Critical for process quality verification
Simulation Time Counter
"Simulation Time": Keeps track of the time elapsed during a simulation run.
- "0 s" indicates ready state or completed simulation
- Accumulates during simulation playback
- Useful for cycle time analysis
- Helps optimize program efficiency
Using This Information
For Diagnostics
- Monitor configuration changes during operation
- Verify TCP speeds match requirements
- Analyze simulation times for optimization
- Check for unexpected state changes
For Optimization
- Use simulation time to estimate cycle times
- Monitor TCP speed for bottlenecks
- Analyze configuration changes for efficiency
- Document optimal configurations
For Troubleshooting
- Compare configurations at error points
- Check speeds at quality issues
- Review simulation vs. actual times
- Identify configuration-related problems
Status Indicators
Common status patterns:
- All zeros: System idle or reset
- Active values: System in operation
- Error codes: System issues present
- Warning values: Approaching limits